
Go to the Home ribbon and click on Conditional Formatting.ģ. Select the whole dataset in three columns by pressing the Ctrl + A keys altogether.Ģ. To use this method, you can follow the following steps:ġ. Setting up a new rule is one of the easiest methods of comparing three columns and determining matching records. =INDEX($B$3:$B$12, MATCH(0, COUNTIF($B$14:B14, $B$3:$B$12)+IF(((COUNTIF($D$3:$D$11, $B$3:$B$12)>0)+(COUNTIF($F$3:$F$12, $B$3:$B$12)>0))=2, 0, 1), 0)) – this is an array formula example – hold down shift and control keys, then press enter and release all keys.ĭownload CONCAT and MATCH NO MATCH practice sheet CONCAT and MATCH NO MATCH Setting Up New Rule Works the same for cells in different columns.Ģ. =IF(AND(A1=A2,A2=A3),"MATCH", "NOMATCH") – to see if values from three cells match. Since custom formulas would be too many to list all here, we'll just have a few examples.ġ.
These can be formed from IF functions, MATCH and NOMATCH arguments, various array formulas, among others. The most advanced and probably the best way for sophisticated analytics is to use custom formulas. Repeat the same for the rest of the names or drag down the green rectangle."" The parenthesis insert space between the names Enter the following formula =CONCATENATE(C2," ",B2," ",A2) and press enter.Let's join the following names using concatenate() function.All the values, unless they are dates or times, will appear joined together, which then allows you to do other operations on a single column such as sort, filter, find medians, average, and, of course, COUNTIF. The formula for concatenating resembles this one: A1&A2&A3. =INDEX(C2:C7,MATCH(B13,A2:A8,0))ī13 contains the product that we are looking for the priceĭownload Index and Match practice sheet Index match practice sheet Concatenate and countĬoncatenating is combining the values of two or more columns together without adding them up. We will use the Index and Match function to obtain the price of Tesla from the table.Įnter the following formula in a blank cell.
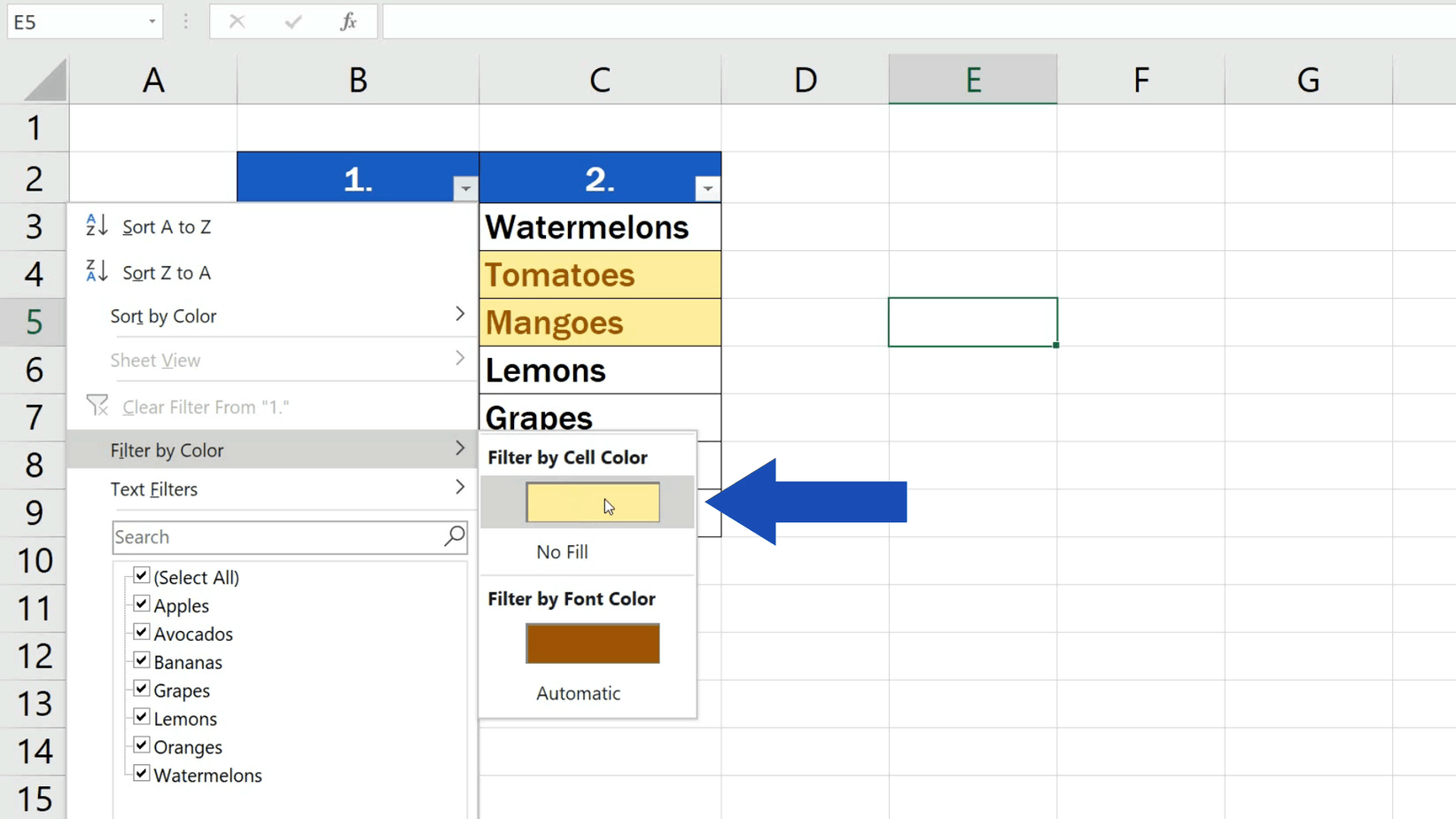
Let's use the data below for our example. Used together, they return values based on the search on a 2D range. Used in the formats = MATCH (first argument, range, second argument) and INDEX (range, argument). Write the following formula to look up the price of Huawei =VLOOKUP(H3,A2:D7,3,FALSE)ģ represent the position of a column with priceįor advanced lookups and returns, the position of a value in a given range.For example, we can check the price of any product on the 3rd column on the following set of data.The lookup value TRUE finds partial matches, while FALSE finds exact matches and returns #NIL if none is found. For example, an index of "3" will have the formula search three columns to the right. The range is the column(s) where you're looking for the value, the index is the column count of that column where you think the answer might be found, which is reckoned on the right of the one you're searching. The criteria is a value or cell with the value you're looking to match. The formula is used in this format: =VLOOKUP(criteria, range, column index, range lookup value). There are various functions you can use to do this, including VLOOKUP, LOOKUP, INDEX, MATCH, and IF functions in various forms. When you're looking for values that match one or more criteria, a lookup operation is what you will do. Choose a fill color for your new formula and hit enter. Go to the Styles tab>Conditional Formatting>New Rule. It works by comparing cell values in two or more lists, depending on how you use it. Use it in the form =COUNTIF(otherlist,firstcellinselectedlist) = 0. NOTE: if the inbuilt formulas for conditional formatting aren't sufficient, the COUNTIF function is a great alternative. click on " Conditional Formatting>Highlight Cell Rules>DuplicatesĤ.Choose the colors for highlighting the duplicate cells by clicking on the drop-down buttonĥ.Press okay, and all the duplicate values will be highlighted with the color you have just selected. Use conditional formatting – Select the columns you wish to compareģ.

You can compare three excel coluns to identify duplicates.ġ.Let's use the following dummy data as an example.Ģ. There are several ideas to help you find duplicates that work differently.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
